Stream media to a channel
Users often need to play video and audio files during online social and business interactions. Video SDK enables you to add media playing functionality to your app. This page shows you how to use the media player classes in Video SDK to enable your users to publish media files to a channel.
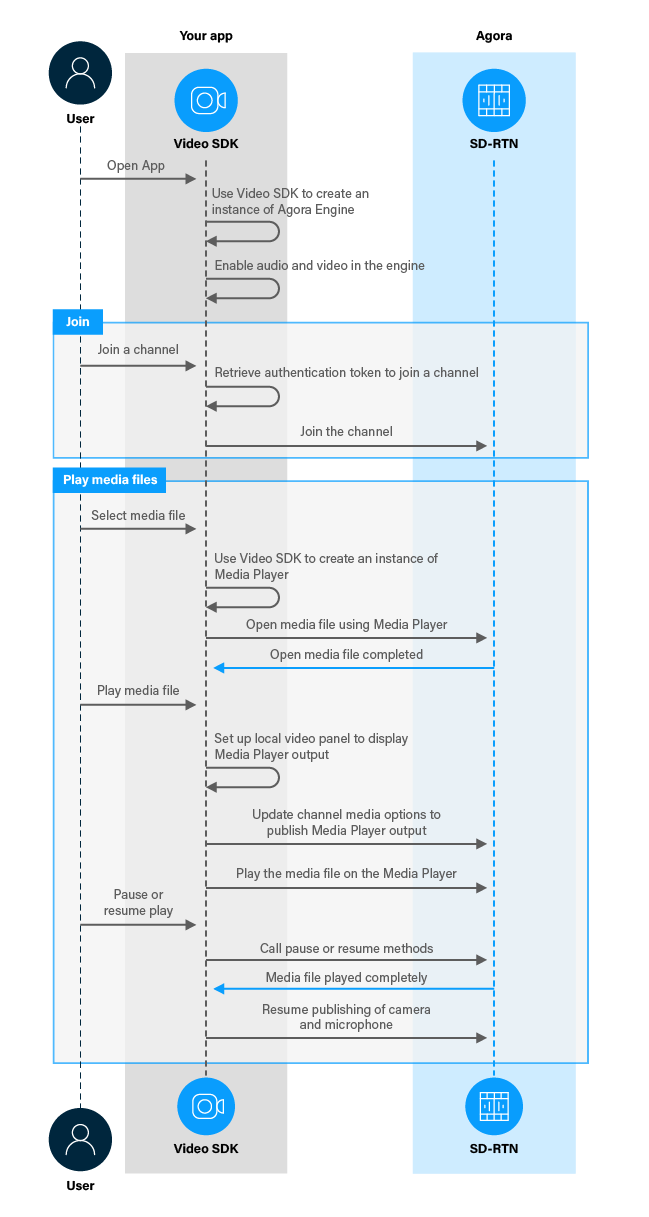
When a user selects a media file to play, you open the media file using a media player instance. When the file is ready to be played, you setup the local video container to display the media player output. You update the channel media options to start publishing the media player stream, then stop publishing the camera and microphone streams. The remote user sees the camera and microphone streams of the media publishing user replaced by media streams.
The following figure shows the workflow you need to integrate media player functionality into your app.
In order to follow this procedure you must have:
- Implemented the SDK quickstart project for Interactive Live Streaming.
- Android Studio 4.1 or higher.
- Android SDK API Level 24 or higher.
- A mobile device that runs Android 4.1 or higher.
-
An Agora account and project.
-
A computer with Internet access.
Ensure that no firewall is blocking your network communication.
To create the environment necessary to implement playing media files into your app, open the SDK quickstart Interactive Live Streaming project you created previously.
This section shows how to use the Video SDK to implement a media player into your app, step-by-step.
In a real-word application, you provide several buttons to enable a user to open, play, pause and stop playing files in the media player. In this page, you use a single Button to demonstrate the basic media player functions. You also add a ProgressBar to display the play progress to the user.
To add the UI elements, in /app/res/layout/activity_main.xml, add the following code before </RelativeLayout>:
_18 android:id="@+id/MediaPlayerButton"
_18 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
_18 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
_18 android:layout_below="@+id/JoinButton"
_18 android:layout_alignEnd="@id/LeaveButton"
_18 android:layout_alignStart="@id/JoinButton"
_18 android:onClick="playMedia"
_18 android:text="Open Media File" />
_18 android:id="@+id/MediaProgress"
_18 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
_18 android:layout_height="5dp"
_18 android:layout_alignEnd="@id/LeaveButton"
_18 android:layout_alignStart="@id/JoinButton"
_18 android:layout_alignBottom="@id/local_video_view_container"
_18 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" />
To setup your project to use the media player APIs and access the UI elements, take the following steps:
-
Add the required libraries
To import the required Agora and Android libraries, in /app/java/com.example.<projectname>/MainActivity, add the following to the list of import statements:
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.IMediaPlayer;
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.IMediaPlayerObserver;
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.data.PlayerUpdatedInfo;
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.Constants.MediaPlayerState;
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.Constants.MediaPlayerError;
_9import io.agora.mediaplayer.data.SrcInfo;
_9import android.widget.Button;
_9import android.widget.ProgressBar;
-
Declare the variables you need
To create and manage an instance of the media player and access the UI elements, in /app/java/com.example.<projectname>/MainActivity, add the following declarations to the MainActivity class:
_10private IMediaPlayer mediaPlayer; // Instance of the media player
_10private boolean isMediaPlaying = false;
_10private long mediaDuration = 0;
_10// In a real world app, you declare the media location variable with an empty string
_10// and update it when a user chooses a media file from a local or remote source.
_10private String mediaLocation =
_10 "https://www.appsloveworld.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/640.mp4";
_10private Button mediaButton;
_10private ProgressBar mediaProgressBar;
-
Access the progress bar
In the onCreate method of the MainActivity class, add the following line at the end:
_1mediaProgressBar = findViewById(R.id.MediaProgress);
To implement playing and publishing media files in your app, take the following steps:
-
Open, play and pause media files
When a user presses the button for the first time, you create an instance of the media player, set its mediaPlayerObserver to receive the callbacks, and open the media file. When the user presses the button again, you play the media file. On subsequent button presses, you pause or resume playing the media file alternately. To do this, add the following method to the MainActivity class:
_41public void playMedia(View view) {
_41 if (mediaButton == null) mediaButton = (Button) view;
_41 // Initialize the mediaPlayer and open a media file
_41 if (mediaPlayer == null) {
_41 // Create an instance of the media player
_41 mediaPlayer = agoraEngine.createMediaPlayer();
_41 // Set the mediaPlayerObserver to receive callbacks
_41 mediaPlayer.registerPlayerObserver(mediaPlayerObserver);
_41 // Open the media file
_41 mediaPlayer.open(mediaLocation, 0);
_41 mediaButton.setEnabled(false);
_41 mediaButton.setText("Opening Media File...");
_41 // Set up the local video container to handle the media player output
_41 // or the camera stream, alternately.
_41 isMediaPlaying = !isMediaPlaying;
_41 // Set the stream publishing options
_41 updateChannelPublishOptions(isMediaPlaying);
_41 // Display the stream locally
_41 setupLocalVideo(isMediaPlaying);
_41 MediaPlayerState state = mediaPlayer.getState();
_41 if (isMediaPlaying) { // Start or resume playing media
_41 if (state == MediaPlayerState.PLAYER_STATE_OPEN_COMPLETED) {
_41 } else if (state == MediaPlayerState.PLAYER_STATE_PAUSED) {
_41 mediaPlayer.resume();
_41 mediaButton.setText("Pause Playing Media");
_41 if (state == MediaPlayerState.PLAYER_STATE_PLAYING) {
_41 mediaButton.setText("Resume Playing Media");
-
Manage media player callbacks
The IMediaPlayerObserver implements media player callbacks. You create an instance of IMediaPlayerObserver and register it with the media player instance. When the player state changes, you take appropriate actions to update the UI in onPlayerStateChanged. You use the onPositionChanged callback to update the progress bar. To create an instance named mediaPlayerObserver, add the following code to the MainActivity class:
_80private IMediaPlayerObserver mediaPlayerObserver = new IMediaPlayerObserver() {
_80 public void onPlayerStateChanged(MediaPlayerState state, MediaPlayerError error) {
_80 showMessage(state.toString());
_80 if (state == MediaPlayerState.PLAYER_STATE_OPEN_COMPLETED) {
_80 // Media file opened successfully
_80 mediaDuration = mediaPlayer.getDuration();
_80 runOnUiThread(() -> {
_80 mediaButton.setText("Play Media File");
_80 mediaButton.setEnabled(true);
_80 mediaProgressBar.setProgress(0);
_80 } else if (state == MediaPlayerState.PLAYER_STATE_PLAYBACK_ALL_LOOPS_COMPLETED) {
_80 isMediaPlaying = false;
_80 // Media file finished playing
_80 runOnUiThread(() -> {
_80 mediaButton.setText("Load Media File");
_80 // Restore camera and microphone streams
_80 setupLocalVideo(false);
_80 updateChannelPublishOptions(false);
_80 mediaPlayer.destroy();
_80 public void onPositionChanged(long position) {
_80 if (mediaDuration > 0) {
_80 final int result = (int) ((float) position / (float) mediaDuration * 100);
_80 runOnUiThread(() -> {
_80 // Update the ProgressBar
_80 mediaProgressBar.setProgress(Long.valueOf(result).intValue());
_80 public void onPlayerEvent(io.agora.mediaplayer.Constants.MediaPlayerEvent eventCode, long elapsedTime, String message) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onMetaData(io.agora.mediaplayer.Constants.MediaPlayerMetadataType type, byte[] data) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onPlayBufferUpdated(long playCachedBuffer) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onPreloadEvent(String src, io.agora.mediaplayer.Constants.MediaPlayerPreloadEvent event) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onAgoraCDNTokenWillExpire() {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onPlayerSrcInfoChanged(SrcInfo from, SrcInfo to) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onPlayerInfoUpdated(PlayerUpdatedInfo info) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
_80 public void onAudioVolumeIndication(int volume) {
_80 // Required to implement IMediaPlayerObserver
-
Configure Agora Engine to publish the media player stream
You use ChannelMediaOptions and the updateChannelMediaOptions method to specify the type of stream to publish. To switch between publishing media player and camera and microphone streams, add the following method to the MainActivity class:
_11private void updateChannelPublishOptions(boolean publishMediaPlayer){
_11 ChannelMediaOptions channelOptions = new ChannelMediaOptions();
_11 channelOptions.publishMediaPlayerAudioTrack = publishMediaPlayer;
_11 channelOptions.publishMediaPlayerVideoTrack = publishMediaPlayer;
_11 channelOptions.publishMicrophoneTrack = !publishMediaPlayer;
_11 channelOptions.publishCameraTrack = !publishMediaPlayer;
_11 if (publishMediaPlayer) channelOptions.publishMediaPlayerId = mediaPlayer.getMediaPlayerId();
_11 agoraEngine.updateChannelMediaOptions(channelOptions);
-
Display media player output locally
Create a VideoCanvas and use it in the setupLocalVideo method of the Agora Engine to show the media player output locally. To switch between displaying media player output and the camera stream, replace the setupLocalVideo() method in the MainActivity class with the following:
_17private void setupLocalVideo(boolean forMediaPlayer) {
_17 FrameLayout container = findViewById(R.id.local_video_view_container);
_17 container.removeAllViews();
_17 // Create a SurfaceView object and add it as a child to the FrameLayout.
_17 localSurfaceView = new SurfaceView(getBaseContext());
_17 container.addView(localSurfaceView);
_17 // Pass the SurfaceView object to the engine so that it renders the local video.
_17 if (forMediaPlayer) {
_17 VideoCanvas videoCanvas = new VideoCanvas(localSurfaceView, Constants.RENDER_MODE_HIDDEN, Constants.VIDEO_MIRROR_MODE_AUTO,
_17 Constants.VIDEO_SOURCE_MEDIA_PLAYER, mediaPlayer.getMediaPlayerId(), 0);
_17 agoraEngine.setupLocalVideo(videoCanvas);
_17 agoraEngine.setupLocalVideo(new VideoCanvas(localSurfaceView, VideoCanvas.RENDER_MODE_HIDDEN, 0));
-
Update the joinChannel method
When you join a channel, you set up the local video panel to initially display the camera output. In the joinChannel(View view) method, replace setupLocalVideo(); with a call to the updated method:
_1setupLocalVideo(false);
-
Clean up when you close the app
To free up resources when you exit the app, add the following lines to the onDestroy method after super.onDestroy();:
_4// Destroy the media player
_4mediaPlayer.unRegisterPlayerObserver(mediaPlayerObserver);
To ensure that you have implemented media player features into your app:
-
Generate a temporary token in Agora Console .
-
In your browser, navigate to the Agora web demo and update App ID, Channel, and Token with the values for your temporary token, then click Join.
-
In Android Studio, open app/java/com.example.<projectname>/MainActivity and update appId, channelName and token with the values from Agora Console.
-
Connect an Android device to your development device.
-
In Android Studio, click Run app. A moment later, you see the project installed on your device.
If this is the first time you run the app, grant camera and microphone permissions.
- Click Join to start a call.
-
Press Open Media File.
After a short while, you see a toast message confirming that the media file is opened successfully.
-
Press Play Media File
You see the media file played both locally and in the web demo app. The progress bar indicates the play progress.
-
Press Pause Playing Media
Media publishing is paused and the camera and microphone publishing is resumed.
-
Press Resume Playing Media
You see that the media file resumes playing.
-
Wait for the media file to finish playing. When the progress bar reaches the end, the media player publishing is stopped and camera and microphone publishing is resumed.
This section contains information that completes the information in this page, or points you to documentation that explains other aspects to this product.
